| LIBROW |
| Professional | Help | Support | Contacts |
Help 6.10
arcoth or arcth — arc-hyperbolic cotangent function
1. Definition
Arc-hyperbolic cotangent is inverse of hyperbolic cotangent function.
arcothx ≡ cothinvxWith the help of natural logarithm it can be represented as:
arcothx ≡ ln[(1 + x) /(x − 1)] /22. Graph
Arc-hyperbolic cotangent is antisymmetric function defined everywhere on real axis, except the range [−1, 1] — so its domain is (−∞, −1)∪(1, +∞). Points x = ±1 are singular ones. Function graph is depicted below — fig. 1.
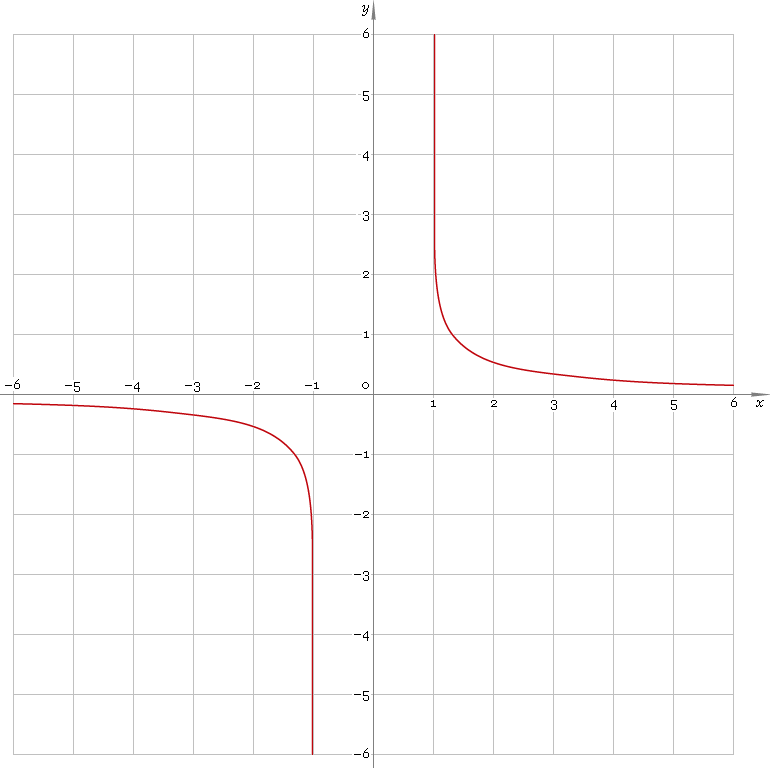 Fig. 1. Graph of the arc-hyperbolic cotangent function y = arcothx.
Fig. 1. Graph of the arc-hyperbolic cotangent function y = arcothx.
Function codomain is all real axis, except 0: (−∞, 0)∪(0, +∞).
3. Identities
Property of antisymmetry:
arcoth−x = −arcothxReciprocal argument:
arcoth(1/x) = artanhxSum and difference:
arcothx + arcothy = arcoth[(1 + xy) /(x + y)]arcothx − arcothy = arcoth[(1 − xy) /(x − y)]
4. Derivative and indefinite integral
Arc-hyperbolic cotangent derivative:
arcoth′x = 1 /(1 − x2)Indefinite integral of the arc-hyperbolic cotangent:
∫ arcothx dx = x arcothx + ln|x2 − 1| /2 + Cwhere C is an arbitrary constant.
5. How to use
To calculate arc-hyperbolic cotangent of the number:
arcoth(−2);To get arc-hyperbolic cotangent of the complex number:
arcoth(−2+i);To get arc-hyperbolic cotangent of the current result:
arcoth(rslt);To get arc-hyperbolic cotangent of the number z in calculator memory:
arcoth(mem[z]);6. Support
Arc-hyperbolic cotangent of the real argument is supported in free version of the Librow calculator.
Arc-hyperbolic cotangent of the complex argument is supported in professional version of the Librow calculator.
| Function 1 √ or sqrt |
|
| Function 2 Γ or Gamma |
|
| Function 3 ∏ or Prod |
|
| Function 4 ∑ or Sum |
|
| Function 5 abs |
|
| Function 6 arccos |
|
| Function 7 arccot or arcctg |
|
| Function 8 arccsc or arccosec |
|
| Function 9 arcosh or arch |
|
| Function 10 arcoth or arcth |
|
| Function 11 arcsch |
|
| Function 12 arcsec |
|
| Function 13 arcsin |
|
| Function 14 arctan or arctg |
|
| Function 15 arg |
|
| Function 16 arsech or arsch |
|
| Function 17 arsinh or arsh |
|
| Function 18 artanh or arth |
|
| Function 19 ceil |
|
| Function 20 conj |
|
| Function 21 cos |
|
| Function 22 cosh or ch |
|
| Function 23 cot or ctg |
|
| Function 24 coth or cth |
|
| Function 25 csc or cosec |
|
| Function 26 csch |
|
| Function 27 exp |
|
| Function 28 fact |
|
| Function 29 floor |
|
| Function 30 I |
|
| Function 31 im |
|
| Function 32 J |
|
| Function 33 K |
|
| Function 34 ln |
|
| Function 35 log or lg |
|
| Function 36 ^ |
|
| Function 37 rand |
|
| Function 38 re |
|
| Function 39 sec |
|
| Function 40 sech |
|
| Function 41 sign |
|
| Function 42 sin |
|
| Function 43 sinh or sh |
|
| Function 44 tan or tg |
|
| Function 45 tanh or th |
|
| Function 46 Y |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||